If you think our summers have been getting hotter every year, you’re not alone. For many of us, the thought of a summer without air conditioning is unbearable. For some people, it might be deadly. But what if there were a way to stay cool in the summer without it?
Getting Cool: The History of Air Conditioning
The desire to provide relief from the heat has been around for centuries, but the first modern air conditioner was invented in 1902. The inventor was a man named Willis H. Carrier. His device was designed as a solution for the Sackett-Wilhelms Lithographing & Publishing Company.
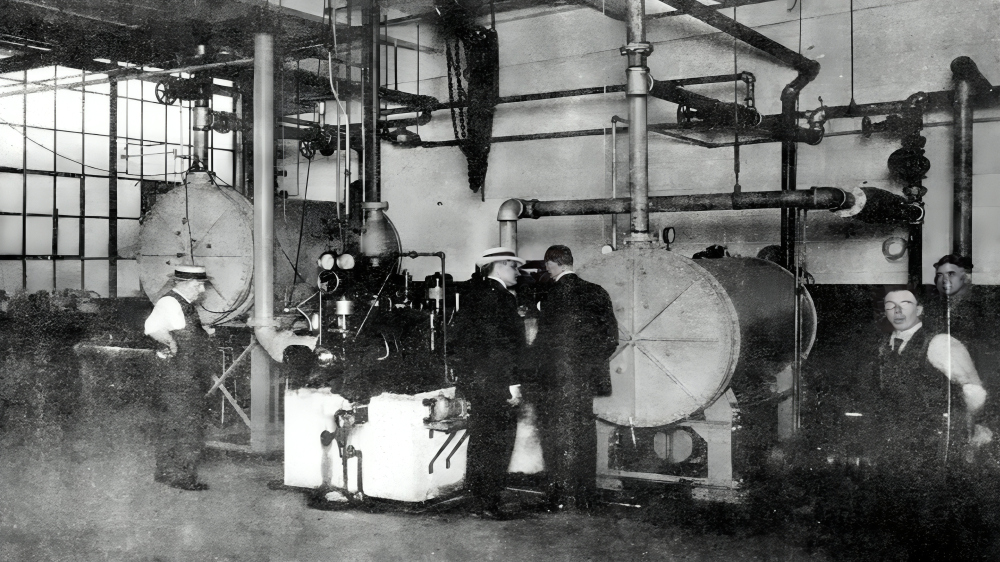
His design allowed the manufacturer to control both heat and humidity. He wasn’t the only inventor to be working on the problem. It wasn’t long before the first in-home air conditioner was installed in the home of Charles Gilbert Gates of Minneapolis.
How Does Air Conditioning Actually Work?
You might be wondering how air conditioning provides relief from summer heat. It starts by taking in air and evaporating the humidity using a coolant. The AC unit uses a blower to disperse warm air over the evaporator. Dry air feels cooler than humid air because cooling is a process of evaporation.

After the humidity has been evaporated, the air conditioner blows it into the area being cooled. AC units include a filter to clean the air before releasing it. The heat from the cooling process is released outside. Excess water from dehumidifying the air is also released.
Air Conditioning in History
The concept of figuring out how to keep homes comfortable has existed from our earliest civilizations. Ancient Egyptians used passive air flow to cool their homes. In Ancient Rome, homes were constructed to protect those who lived there from the heat.
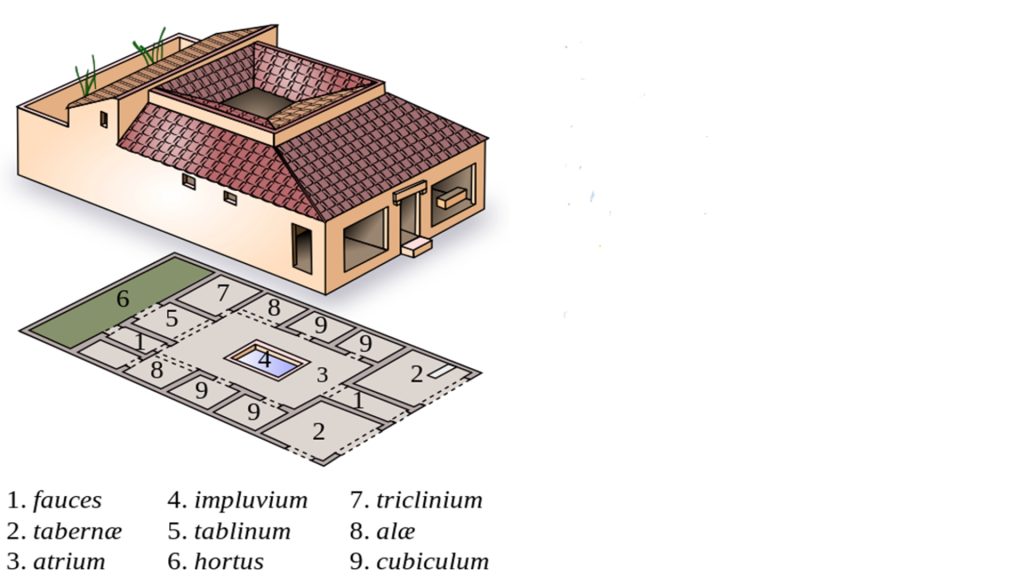
The system created by the Romans was a form of radiant cooling. They circulated water from the Roman aqueducts through the walls and floors. The flow of water reduced the temperature, keeping the home cooler than the outside temperature.
Cob and Stucco and Clay, Oh My!
Sometimes, materials alone can make a difference in the inside temperature of a building. Cob is one of the oldest building materials in the world. Typically made from a mix of dirt and straw, it’s known by many names around the world, including stucco.

In most areas of the world, there’s some variation of a clay-based construction material. Sometimes it’s made into bricks. Sometimes it’s piled in layers and allowed to dry before adding more material. There’s a reason that so many homes in hot climates are built using materials like these!
Ice, Ice Baby
Some of the earliest attempts at mechanical air conditioning involved putting ice in front of a fan. People cut large blocks of ice during the winter and stored them in ice houses. During the summer, the blocks were used to cool homes.
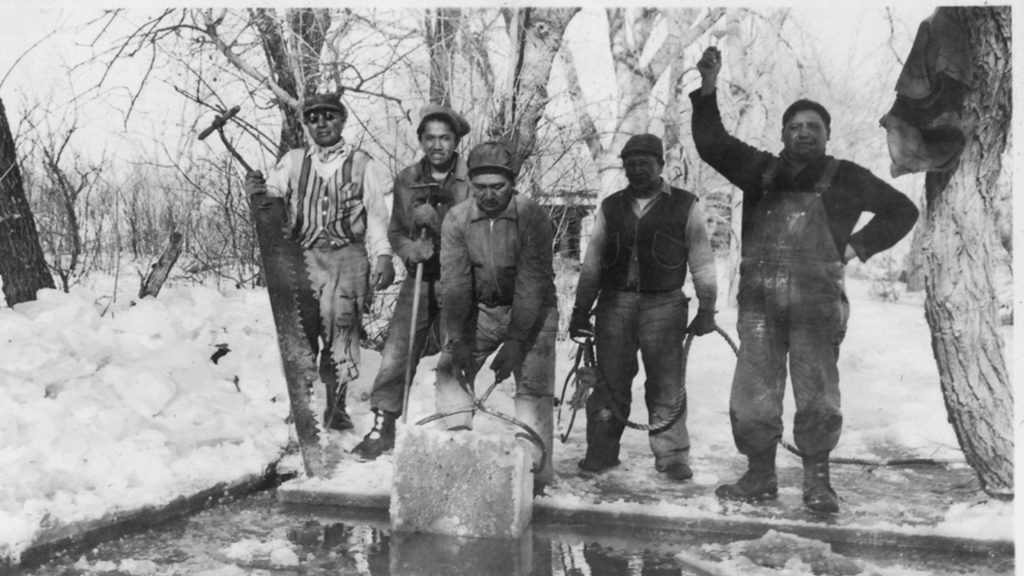

The principle behind using ice to cool down a room is simple. As ice melts, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air. The effect isn’t as dramatic as it would be with a mechanical air conditioner. But, in the heat of summer even a few degrees can make a big difference.
How Air Conditioning Changed The World
The invention of air conditioning had a huge impact on the world. Things that weren’t possible without AC became possible. These changes have affected medicine, entertainment, and even the places we choose to live-not to mention the effect on our electric bills!

If you live in a hot climate or simply dislike the summer heat, then it’s likely that access to AC has been something you value. You might not realize that the invention of AC has literally changed the world in a variety of ways.
No AC, No Summer Blockbusters?
If you’ve ever gone to the movies to cool off on a hot day, you’re not alone. In fact, that’s one of the reasons that going to the movies became popular. AC used to be very expensive and was only installed in large public buildings that could afford it.

During the years when AC was rare, people took advantage of it wherever they could find it. Because folks went to the movies to cool off, theaters and movies earned more revenue during the hot months of the year-and that’s how the summer blockbuster was born.
AC And Modern Medicine
Lab experiments require carefully controlled conditions. High temperatures in a lab can be damaging since they can disrupt experiments. The same is true of humidity that’s too high. The invention of air conditioning did a lot for modern medical research.
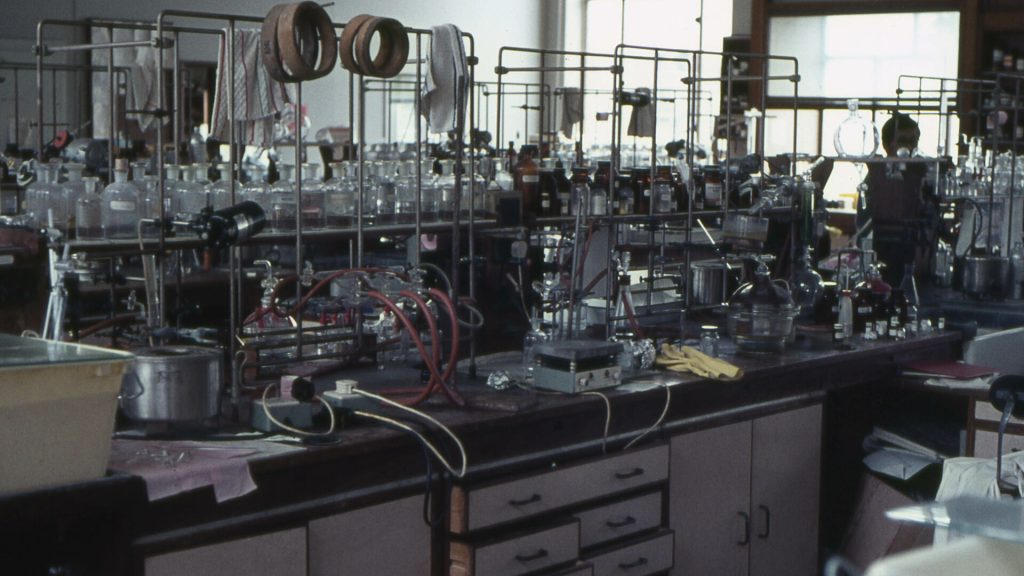
Not only did the invention of AC help laboratories control temperatures, it helped in other ways too. One of the most important is that it allowed for control of ventilation. Researchers could work in safe spaces while handling potentially dangerous chemicals.
Living In Las Vegas (Or Dubai)
Another thing that air conditioning has done for us is to make it possible to live in some of the hottest places on Earth. Some people mind the heat more than others. For them, it’s only possible to live in Las Vegas if they have air conditioning.
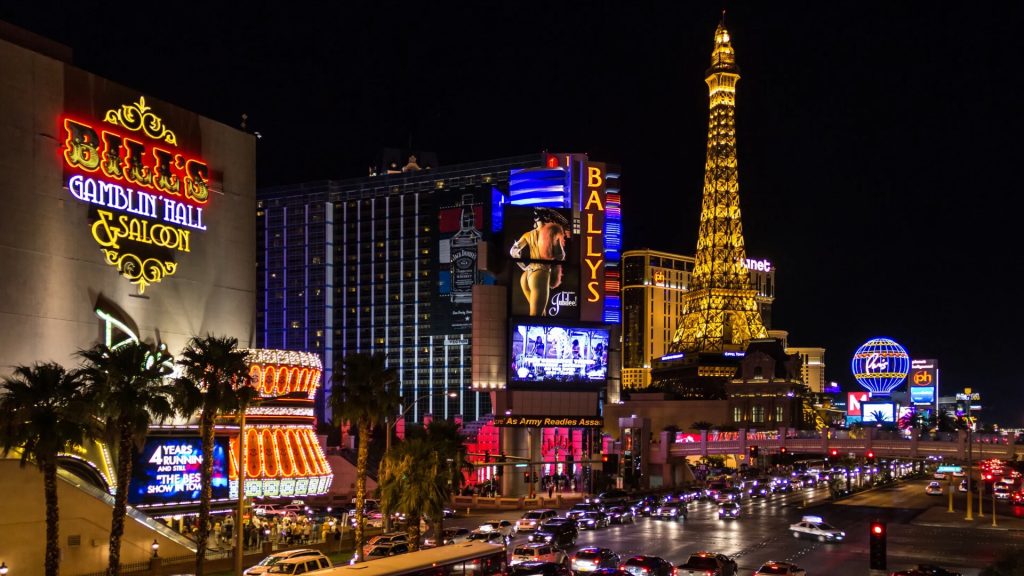

The invention of AC means that people living in hot climates have a comfortable place to work and sleep. It’s easy to imagine the population of Vegas or Dubai being a lot smaller if air conditioning weren’t readily available.
Have Temperatures Increased Air Conditioning Use?
The use of air conditioning is on the rise. 77% of US households had air conditioning in 2001. That number has risen to 88% as of 2023. Those numbers aren’t surprising. The average temperature in the United States has risen nearly two degrees in that time.
As temperatures rise, it becomes increasingly uncomfortable to live without air conditioning. It used to be that in some places, it was normal not to have air conditioning. Now, even people who live in northern areas prefer to have air conditioning to combat summer heat.
What’s the Deal with Coolant?
When people talk about air conditioning, a top concern is the coolant used to lower temperatures. For a long time, Freon was the most common coolant in air conditioners and refrigerators. It’s also used in automotive cooling and other places.

The primary concern around the use of Freon is that it has played a role in climate change. Specifically, it’s believed that releasing Freon into the atmosphere has been at least partly responsible for the hole in the ozone layer.
Air Conditioning And The Environment
There’s a lot of concern about the impact that human beings have had on the world’s climate. As we release more carbon dioxide and other substances into the air, the earth grows warmer. Air conditioning may also have played a role.
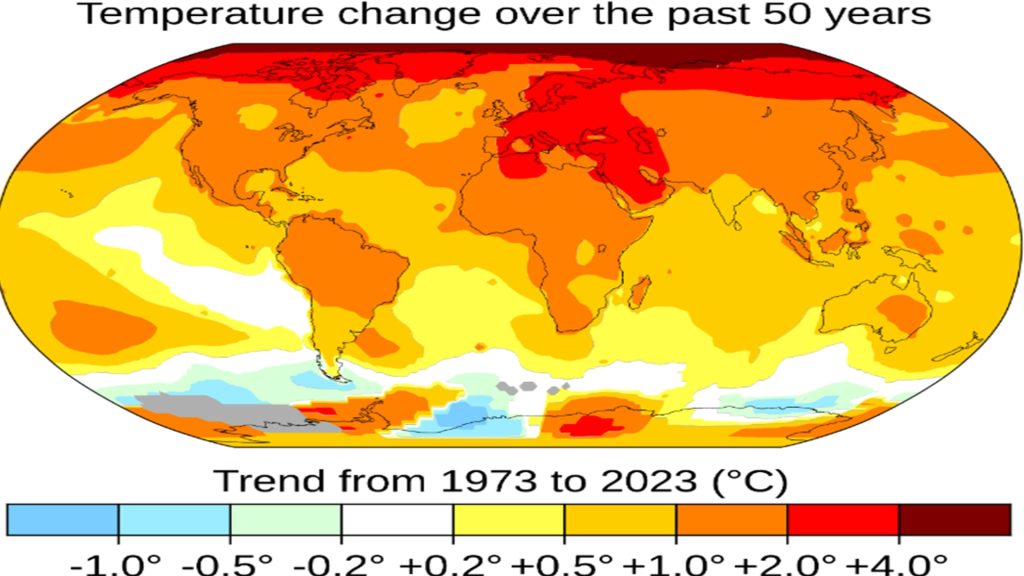
In many areas of the world, the temperature increase in the past 50 years has been dramatic. While a swing of a few degrees might not seem like much, people everywhere are feeling the impact. Finding eco-friendly alternatives to AC is a priority for many.
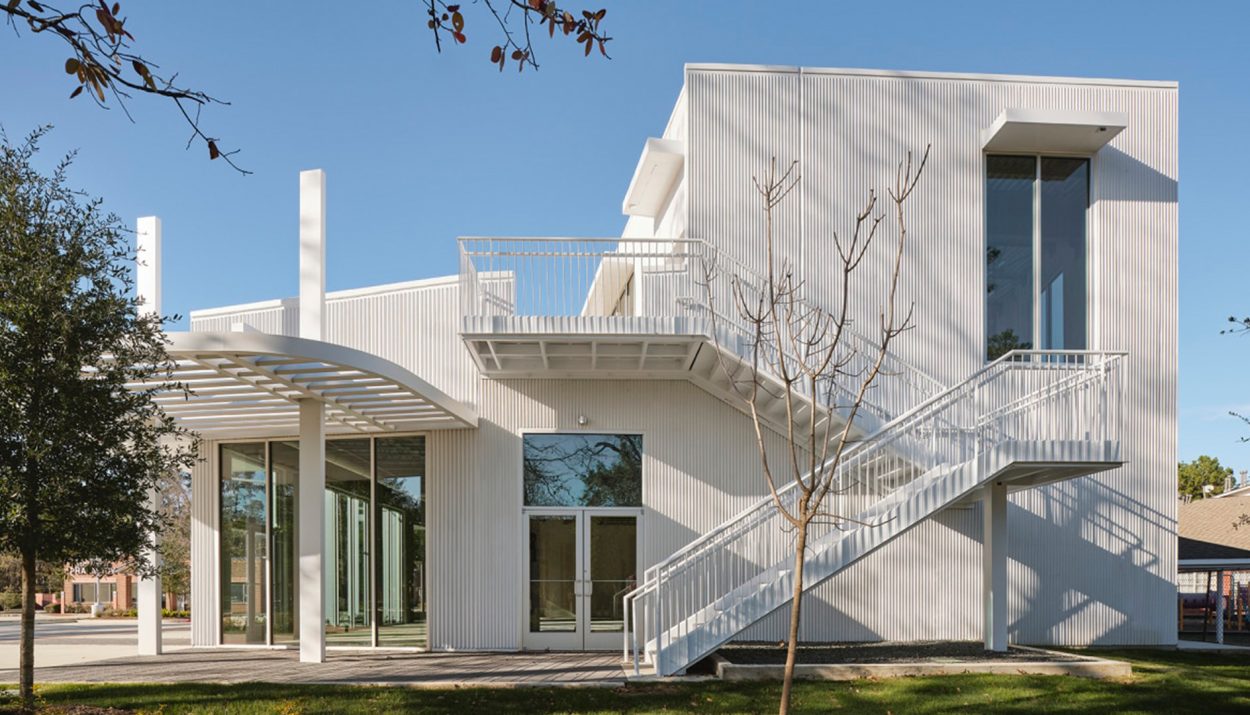
How Engineers and Architects Can Save Us
It has become clear that we need to explore alternatives to air conditioning. One recent development comes from architectural firm Modu and engineering firm Transsolar. Together, they designed and built a medical building that uses ridged concrete.
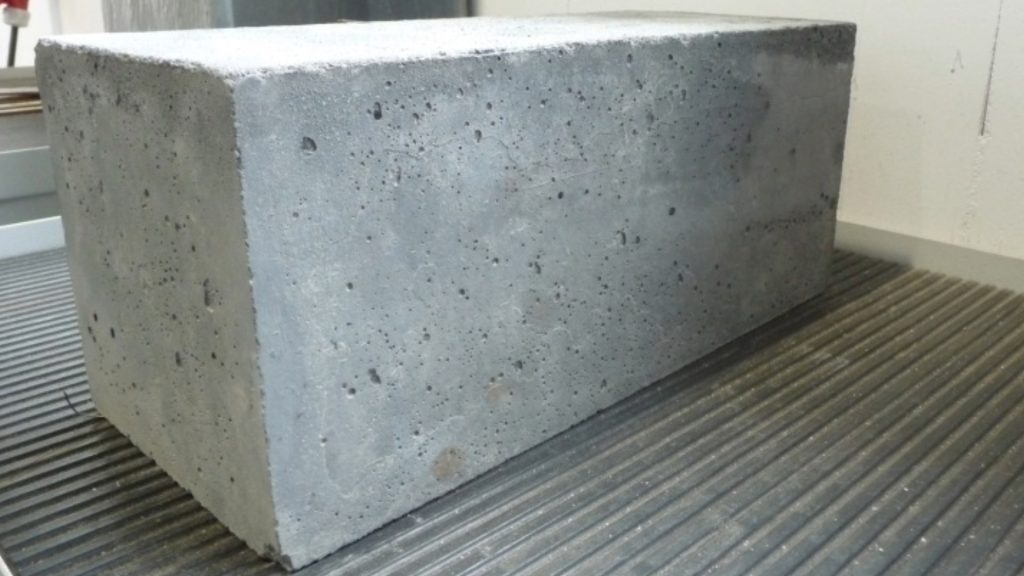

The idea behind the ridged concrete is that it gives the building more surface area to disperse heat. Tests have revealed that the temperature inside the building is approximately 14 degrees cooler than the outside temperature. Not as cool as air conditioning, but still impressive!
Cool Dirt: The Power of Geothermal Cooling
Manipulating concrete isn’t the only way to cool buildings without using air conditioning. Geothermal heating and cooling is a process that can both heat buildings up and serve as an alternative to AC. These systems are far more efficient than traditional AC.
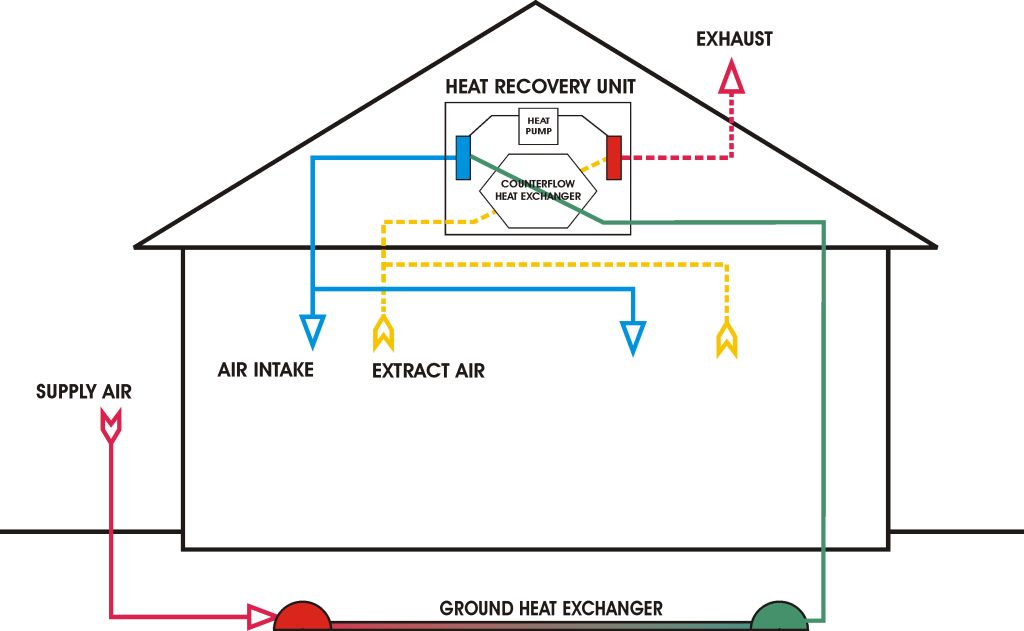
In terms of saving energy, geothermal systems can do a lot. They use between 25% and 50% less electricity than air conditioning. Even in a very hot climate, the combination of a geothermal system with energy-efficient building materials could rival the power of air conditioning. They’re certainly options worth exploring.
DIY Air Conditioning: The Swamp Cooler
What happens if you don’t have AC or a home that’s been built to keep you cool? One option is the DIY air conditioning known as the swamp cooler. Also known as an evaporation cooler, It’s a cooling system that you can create yourself with just a fan and a wet cloth.

Fans cool you down by keeping the air moving. If you soak a cloth with cold water and place it in front of the fan, you’ll have a swamp cooler. The light spray of water creates a natural cooling process of evaporation. The result is a feeling of coolness.
Up And Out: The Attic Fan
Another low cost alternative to air conditioning is to use an attic fan. When properly placed, an attic fan can pull hot air out of the house. Since hot air naturally rises, it makes sense to use a fan in the highest (and hottest) part of your home.

When the fan is facing outward, it pulls the hot air from the attic and pushes it out of the house. In this way, it can lower the temperature inside and make it more comfortable. If you don’t have central air, an attic fan can do a lot to keep you cool.
The Future With (Or Without) AC
How do you see the future? With rising temperatures, you may think that more AC is the answer. But some of the greatest minds in the world are thinking of solutions that can keep us cool without hurting our planet.

When it’s not too hot out, why not experiment with a swamp cooler or an attic fan? Or, if you’re building a home, consider cooling materials such as ridged concrete or stucco to lower the temperature naturally to stay cool in the summer.






